
While it is one thing to test Automated Vehicles (AVs) in controlled environments, the end goal of SHOW is to test AVs in real life while safeguarding efficiency and safety. To facilitate a smooth integration of AVs into a real driving environment, SHOW partner SWARCO has led task 8.3, which focuses on developing solutions for collaborative Traffic Management.
Traffic Management offers guidance to travelers and road users, providing information (for example via navigation services) on the traffic status and on the conditions of the road network. It detects emergencies and incidents, which can be unforeseeable or planned (e.g., accidents, road works, adverse weather conditions, strikes, holiday traffic peaks etc.) and implements response strategies to ensure safe and efficient use of the road network, also across borders.
Traffic Management is key to accommodate the movement of AVs in real mixed traffic environments: AVs need to be aware of everything happening on the route ahead, also beyond their own sensors.
Under the task, SWARCO analysed current Traffic Management practices at all demo sites, while also exploring potential interactions between Traffic Management, road infrastructure, and AVs. Overall, the goal of this task is to promote and implement interactive Traffic Management, considering close cooperation between public and private partners and between vehicles and infrastructure.
Traffic Management 2.0
Traffic Management is currently facing a large transformation, mainly pushed by the improvement of existing infrastructure (such as smart traffic lights and connected cameras), gradual introduction of new generation vehicles with increased connectivity between each other and to the infrastructure (thanks to 5G and the new C-ITS messages that permit a Vehicle-2-vehicle communication in real time for coordinated manoeuvres, for example for changing lanes), and by the development of new technological systems and procedures to better manage traffic operations and to offer new types of passenger and freight services.
One key element in D8.3 is Traffic Management 2.0 (TM2.0), which stands for a collaborative concept for Traffic Management and Control between public and private partners and between vehicles and infrastructure, and which will be implemented in the SHOW demo sites. The TM2.0 can be considered an update of current Traffic Management practices, in which travelers and goods by using new technologies (such as AVs) and sensors become entirely part of the data supply chain. Task 8.3 provides recommendations on how to increase interactions among actors, with the aim to improve safety and network wide optimisation.
The concept of TM2.0 is the evolution of current Traffic Management practices, which are for now mainly based on loop detectors (that detect vehicles e.g. at a traffic light) and static traffic data used by Traffic Management centres. TM2.0 builds upon the deployment of connected vehicles and travelers to achieve convergence of mobility services and Traffic Management, combining actions of the individual travelers into a collective mobility system. This way, TM2.0 connects the innovative developments in the vehicle and on the road while improving the value of the service and at the same creating new business opportunities.
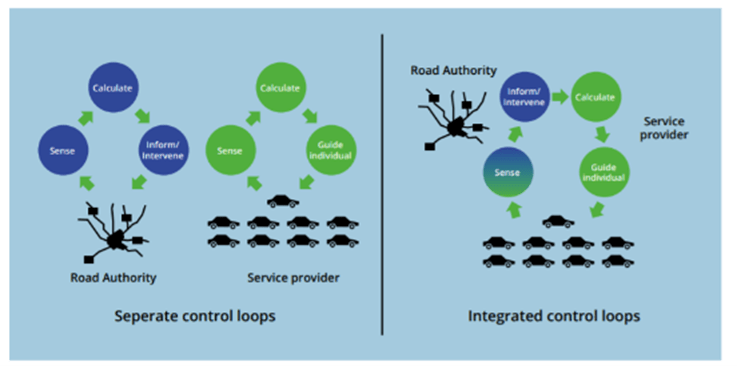
Figure 1: TM2.0 concept with integrated control loops (right)
In the demo sites, several Traffic Management services have been identified, with various degrees of interaction between the vehicles and the road infrastructure. The following TM 2.0 (a collaborative concept for Traffic Management and Control between public and private partners and between vehicles and infrastructure) services have been chosen based on the technologies investigated until now and which are most promising for implementation in the near future. Furthermore, an attempt was made to identify those services that could be combined with the infrastructure of the SHOW demo sites in order to have greater integration between the sites and the services proposed.
The following Traffic Management services are described in the deliverable:
- Traffic Light Assistance
- Green Light Priority for authorized vehicles
- Platooning strategies
- Information on charging stations
- Parking Information
- Dynamic strategies for Opening/closure of LTZ (Limited Traffic Zone)
- Proactive road maintenance
- Strategies for Collaborative Traffic Management
- Operational Design Domain (ODD) Management
Conclusions and outlook
In conclusion, the rise of connected and automated driving is pushing for an evolution of Traffic Management systems. Especially highly automated vehicles need to be aware of everything happening on the route ahead, also beyond their own sensors. Therefore, in the future, Traffic Management should be able to support the automated vehicles’ interaction and communication with their surroundings, providing the necessary data to increase road safety and efficiency. Connected and automated vehicles, with their advanced sensing systems, are also expected to enable the provision of more reliable and efficient Traffic Management services, with high quality and detailed data on the status of the road network (e.g., road conditions, traffic state and incidents that they encounter while driving, etc.).
The vision is to work towards establishing collaborative Traffic Management practices that also include new technologies such as AVs. Overall, this requires a strong cooperation of the public and private sectors working in the Traffic Management ecosystem. Traffic Management related data needs to be exchanged and translated into intelligent decisions and high-quality and safe services, with the overall goal of enhancing the safety and efficiency of traffic for all road users.
For more info on D8.3, please contact alberto.bellini[at]swarco.com.